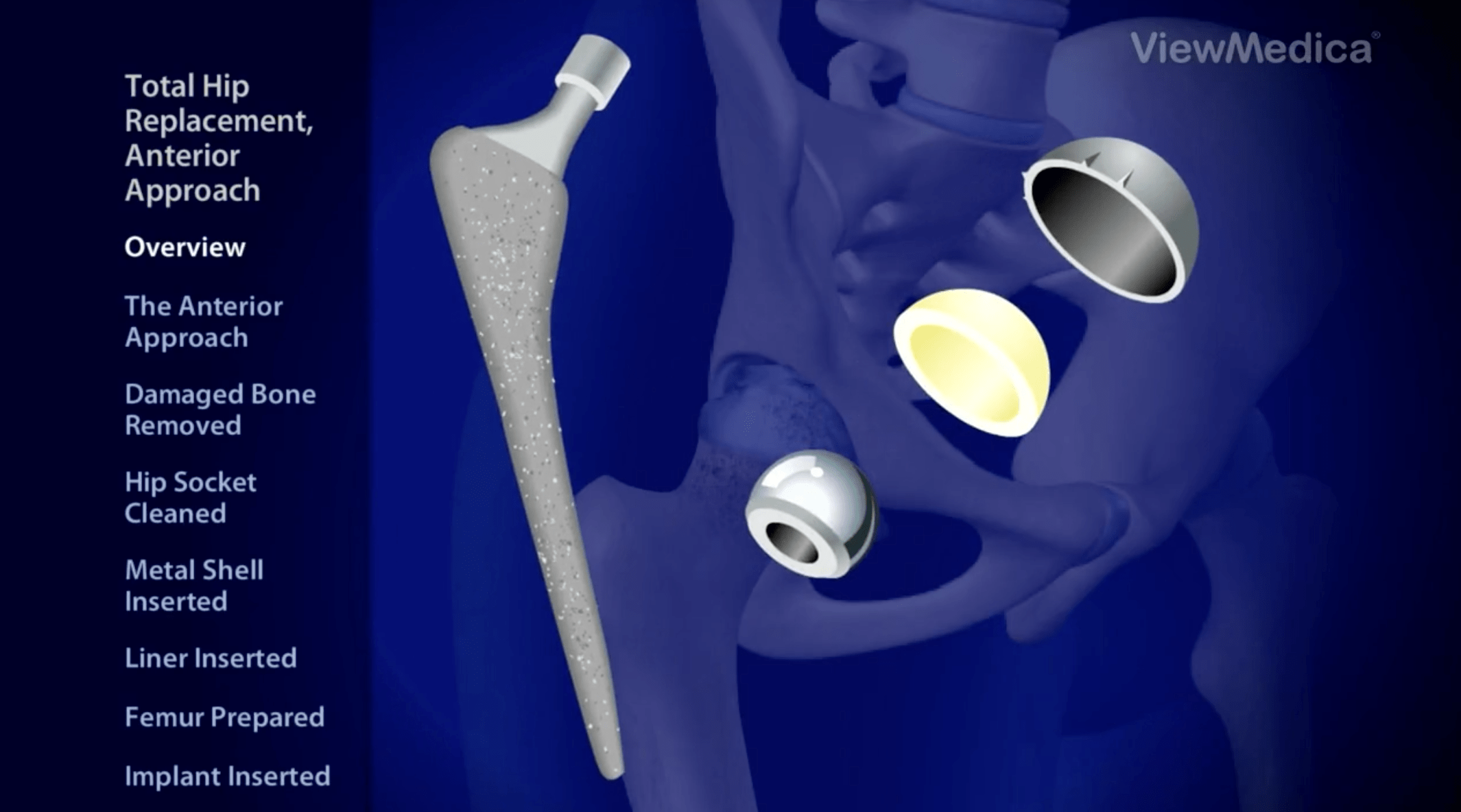
Learn about the dynamics of physical mobility, hip anatomy and function to gain a deeper understanding of body health.
How can the hip joint be damaged?
- Wear and tear: Regular activities and aging can lead to the deterioration of the hip joint, especially the cartilage.
- Injuries: Hip fractures, dislocations, and muscle strains are common injuries that can impair hip function.
- Diseases: Conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to hip pain and stiffness.